Differences and Applications of UWB Positioning Technology and GPS Positioning
When it comes to positioning technology, most people first think of GPS navigation applications. However, with the continuous development of technology, positioning technology has become diversified. UWB modules, as an emerging positioning technology, are gradually emerging and showing tremendous potential in specific fields. Below is a brief introduction to the differences and applications of UWB positioning systems and GPS positioning systems.
UWB Positioning System: Features and Applications
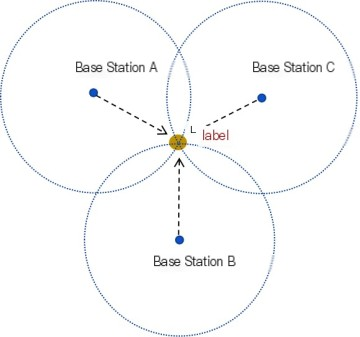
The UWB positioning system consists of multiple UWB modules forming base stations and positioning object tags. When a positioning tag appears within the base station's positioning range, each base station receives the tag signal and determines the distance between the tag and the base station based on the time difference of arrival (TDoA) or phase difference of arrival (PDoA) of the signal. The position of the tag is determined by the distance between each base station and the tag, known as UWB triangulation positioning.
The UWB signal has an extremely wide bandwidth, enabling high-speed data transmission and excellent anti-interference capabilities, allowing it to work reliably in complex electromagnetic environments. Therefore, UWB modules are widely used in smart homes, industrial automation, indoor navigation, and other fields, providing high-precision positioning and reliable data transmission support for these scenarios. The characteristics and applications of UWB positioning can be summarized as follows:
Positioning Principle: Calculate the position by measuring the time difference or phase difference of arrival of the tag signal using multiple UWB modules set up as base stations, such as triangulation.
Positioning Accuracy and Range: Achieve centimeter-level high-precision positioning within a specific range.
Ultra-Wideband: The signal bandwidth is extremely wide, capable of providing high data transmission rates, typically exceeding 500 MHz.
Anti-Interference: With its unique spectrum spreading technology, UWB signals have strong anti-interference capabilities.
Application Scenarios: Suitable for indoor positioning, object tracking, and other scenarios that require high positioning accuracy and data transmission rates.
Characteristics and Applications of GPS Positioning System
The GPS satellite positioning system operates through a combination of satellites, ground control stations, and receiving devices to achieve positioning and navigation. The satellite system emits navigation signals around the Earth, which are transmitted to the Earth in the form of radio waves. Users then utilize receiving devices (GPS modules) to receive data transmitted by multiple satellites, including satellite positions and the time stamps of transmitted signals, to calculate their own position, velocity, and time for positioning and navigation. This calculation requires receiving signals from at least three satellites to determine the three-dimensional coordinates (longitude, latitude, altitude) of the position on Earth. The ground control station serves as a main control station used to monitor and manage the operation of GPS satellites, performing orbit corrections and time synchronization to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the satellites.
In the GPS satellite positioning system, in addition to satellites, ground control stations, and receiving devices (GPS modules), data transmission units (DTUs) and cloud servers are also required to analyze data for remote transmission, storage, and application purposes.

GPS positioning technology is a global positioning technology based on satellite positioning systems. Its main advantage lies in its ability to cover the entire globe and provide relatively accurate positioning information, typically achieving meter-level or decameter-level accuracy. GPS modules are suitable for outdoor environments, such as vehicle navigation, aviation, marine navigation, and outdoor sports. The characteristics and applications of GPS positioning technology can be summarized as follows:
Positioning System: Utilizes satellite signals for global positioning, relying on satellite signals and ground control main stations for positioning.
Positioning Accuracy and Range: Global coverage, typically achieving meter-level or decameter-level accuracy, but susceptible to signal obstruction and multipath effects.
Communication Features: Primarily used for positioning and time synchronization, with limited communication capabilities and not suitable for high-speed data transmission.
Application Scenarios: Outdoor navigation such as vehicle navigation, aviation, and marine navigation.
In conclusion, as positioning technology continues to evolve and application demands become more diverse, UWB modules are emerging as a new and competitive alternative to traditional GPS modules while also complementing them. In the future, with further development and maturity of UWB technology, it is expected to demonstrate unique advantages and application potential in more fields, bringing greater convenience and innovation to people's lives and work.
 +86-755-23080616
+86-755-23080616
 sales@nicerf.com
sales@nicerf.com
Website: https://www.nicerf.com/
Address: 309-314, 3/F, Bldg A, Hongdu business building, Zone 43, Baoan Dist, Shenzhen, China