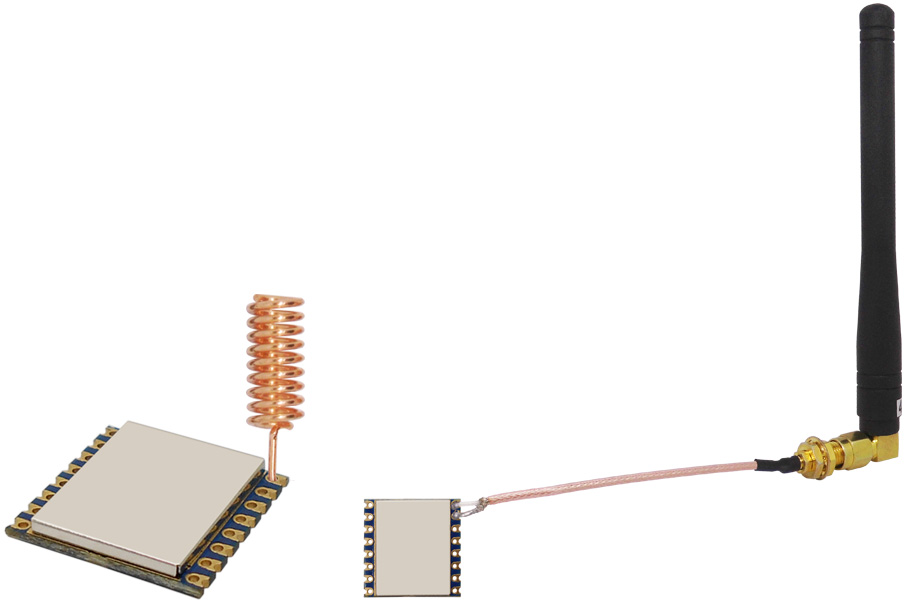
Attention! Wireless modules not connected to the antenna not only affect the transmission distance
In modern wireless communication, wireless modules play a crucial role and are widely used in fields such as the Internet of Things, smart homes, and industrial data collection. Wireless modules typically need to be used in conjunction with antennas to ensure effective signal transmission and reception. So, when a wireless module is not connected to an antenna, does it only affect the module's transmission distance? The answer is no; the impact on transmission distance is just one aspect. It may also lead to various other issues, and in severe cases, could even damage the module itself. Below are some problems that may arise when a wireless module is not connected to an antenna.
Reduced Communication Distance and Data Transmission Quality
The effective communication distance of a wireless module typically depends on its transmission power and signal propagation capability. Without an antenna, the signal cannot radiate properly, leading to a significant reduction in communication distance. For low-power modules, their already limited effective communication distance may drop to nearly zero. Even for high-power modules, while theoretically capable of covering larger ranges, their signal coverage ability will also be greatly compromised in the absence of an antenna. Additionally, data transmission may experience delays and packet loss, severely affecting user experience.
This phenomenon is particularly evident in practical applications. For instance, in IoT devices, the stability of the signal and transmission distance are crucial for system reliability; lacking an effective antenna can render the system inoperable.
Battery loss
When a wireless module operates without an antenna, its energy conversion efficiency significantly declines. The energy from the transmitter fails to be effectively converted into radiated signals, resulting in substantial energy wastage. This issue is more pronounced for high-power modules, where prolonged ineffective transmission not only affects the device's energy efficiency but may also shorten battery life, increasing user costs.
Furthermore, the power loss in the module when there is no antenna can impose an additional burden on the power supply, causing it to overheat and potentially leading to other electrical faults.
Signal Reflection and Standing Waves
When a wireless module is operating, the transmitted signal needs to radiate through the antenna into the air. If the module is not connected to an antenna, the transmitted signal will not radiate effectively and will instead be reflected back into the module. The presence of this reflected signal can create standing waves, increasing the voltage inside the module. This high voltage can stress the RF components and power amplifier within the module, potentially causing overheating, failure, or even burnout.

Of course, the module can employ effective protection mechanisms; for example, G-NiceRF full-duplex intercom module uses a watchdog chip to provide over current and over voltage protection. However, this does not mean that modules with protection mechanisms can operate without an antenna. While such protection can help extend the device's lifespan, it cannot completely eliminate the other risks associated with operating without an antenna.
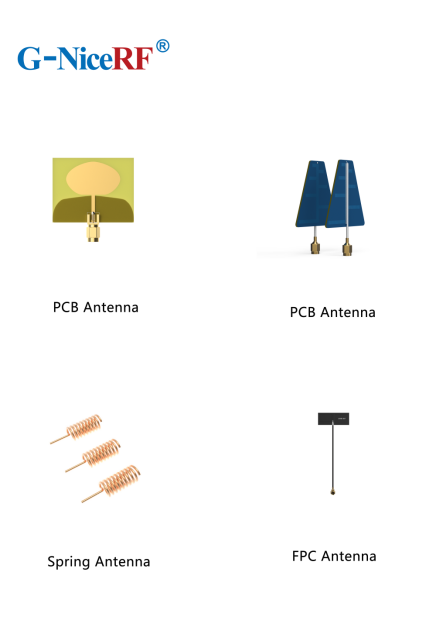
To avoid losses caused by the absence of an antenna, users are advised to prioritize the installation and maintenance of antennas when using wireless modules. The types and gains of antennas for wireless modules vary, so suitable antennas should be chosen based on application needs and the module's operating frequency. G-NiceRF can provide various antennas to match different applications of the module, as detailed in the following table.
Type | Product | Features | Gain | Frequency band |
| |
Compact size, easy installation, and aging resistance make it suitable for various terminal devices. |
2.15~3dBi |
150MHz/315~365MHz 433/470/868/915MHz 2.4GHz
|
Sucker Antenna | |
No mounting brackets or additional equipment are needed; it can simply be attached to a flat surface. |
3~5.5dBi |
315/433/470/490MHz 868/915MHz 2.4GHz/4Ghz |
Built-in modules are low-cost and do not require multiple adjustments | ||||
| | Low-cost ultra-wide band omnidirectional antenna.
|
3dBi |
3700-8000MHz (UWB Module antenna) 433MHz
|
Gain Yagi Antenna | |
High gain, interference-resistant, and wide bandwidth |
11dBi |
433/915MHz
|
IPEX Antenna
| |
Good signal direction and strong anti-interference |
1dBi |
2.4GHz |
GPS Antenna |
|
Built-in active antenna, high gain and wide main lobe beam characteristics.
|
18/3dBi |
1575.42MHz 1561.098MHz |
In summary, wireless modules face multiple challenges when operating without an antenna, including issues with communication distance, battery impact, and over voltage risks due to signal reflection and standing waves. Whether for low-power or high-power modules, promptly connecting the appropriate antenna is crucial for ensuring normal operation.
 +86-755-23080616
+86-755-23080616
 sales@nicerf.com
sales@nicerf.com
Website: https://www.nicerf.com/
Address: 309-314, 3/F, Bldg A, Hongdu business building, Zone 43, Baoan Dist, Shenzhen, China